Chapter Five - Exercise and Physical Activity
Physical Activity (PA): “Any bodily movement produced by the contraction of skeletal muscles that results in a substantial increase in energy expenditure.”
Physical Fitness: “Multidimensional concept defined as a set of attributes/skills that people possess or achieve that relates to the ability to perform physical activity.”
Exercise: “Type of Physical Activity consisting of planned, structured, and repetitive bodily movement done to improve and/or maintain one or more components of physical fitness.” - Caspersen et al 1985
The ability of contractile tissue to produce tension and a resultant force according to the demands placed on that muscle.
The greatest measurable force exerted by a muscle to overcome resistance during a single maximum effort.
The maximum force that a muscle or muscle group can generate in a minimum time. Its development depends on the right balance between speed and strength on a specific skill that requires explosiveness.
Work = (force x distance)/time
Manual testing: Application of increasing resistance to produce a concentric contraction of the muscle tested until a maximum contraction is reached.
Isometric testing allows for structural differentiation because joint motion it prevented and the test is isolated to the muscle.
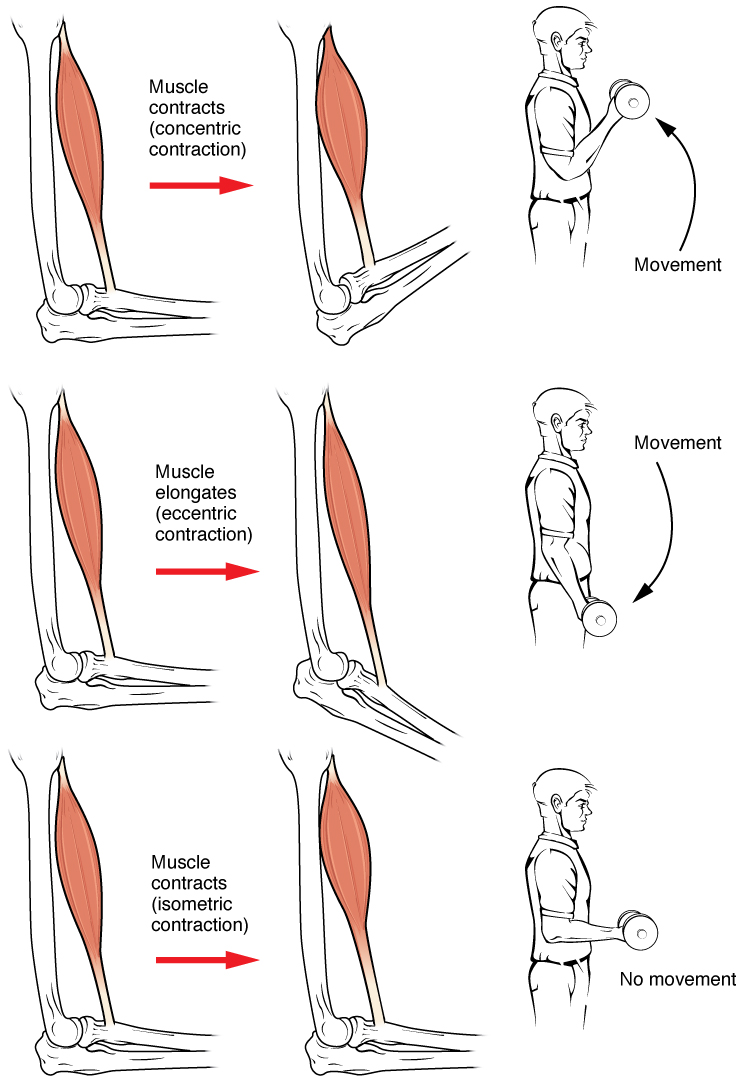
Isokinetic contraction is one in which a muscle shortens as it contracts but, unlike an isotonic contraction, (consistent speed).
Isometric contraction, the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement in the angle of the joint. (the muscle is in consistent length)

When WB position is assumed, and body moves over a fixed distal segment i.e., the hand (for arm mvt) of foot (for leg mvt) is fixed in space and cannot move. The extremity remains in constant contact with the immobile surface, usually the ground or base of a machine.

When Non-Weight Bearing (NWB) position is assumed, and the distal segment (hand or foot) moves freely during exercise.
Limb movement occurs distal to moving joint due to contraction of muscles that cross the joint.
Endurance: The ability to perform low intensity, repetitive or sustained activities over a prolonged period of time.
Anaerobic Exercise: Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen; anaerobic means “without oxygen”. In practical terms, this means that anaerobic exercise is more intense, but shorter in duration than aerobic exercise.

Endurance Exercise: Endurance training is the act of exercising to increase endurance. The term endurance training generally refers to training the aerobic system as opposed to the anaerobic system.

Resistance Training: Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises which are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the use of weights but can take a variety of different forms.

Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling of increased muscle control, flexibility, and range of motion.
