Chapter Four - Development across the life Span

Cognitive development refers to how a person perceives, thinks, and gains understanding of his or her world through the interaction of genetic and learned factors. Among the areas of cognitive development are information processing, intelligence, reasoning, language development, and memory.
Early childhood is a time of forming an initial sense of self. A self-concept or idea of who we are, what we are capable of doing, and how we think and feel is a social process that involves taking into consideration how others view us.
Physical growth refers to an increase in body size (length or height and weight) and in the size of organs. From birth to about age 1 or 2 years, children grow rapidly. After this time, growth slows.
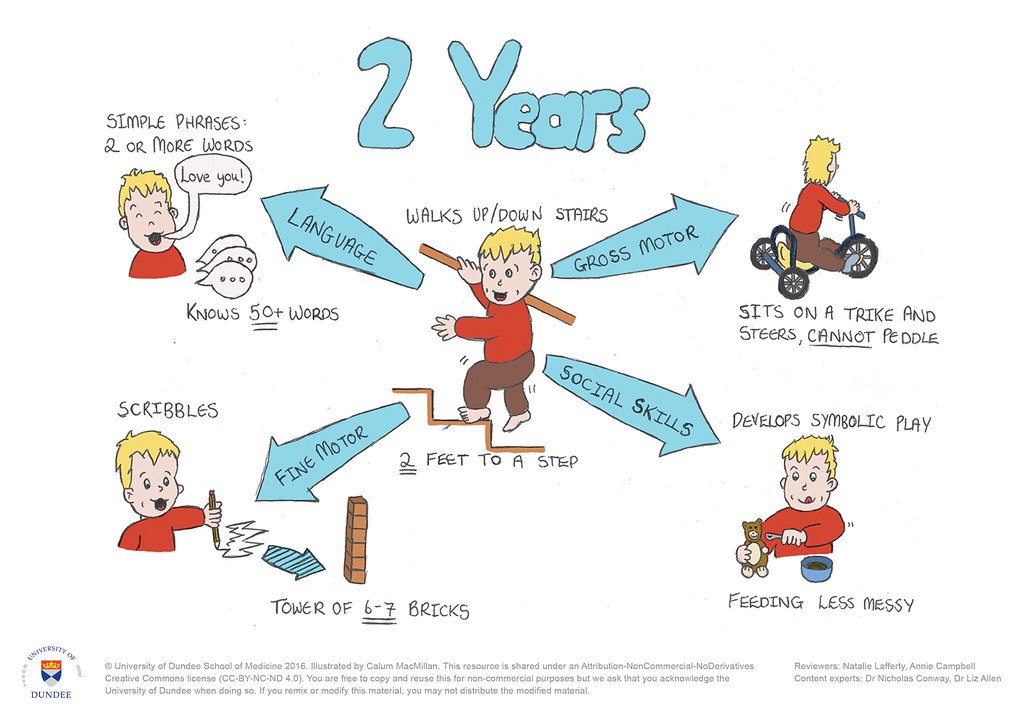
Physical developmental Milestones are the physical attributes that one forms and they progress from gross motors skills (large movements of large joints) and fine motor skills (small movements involving small joints).
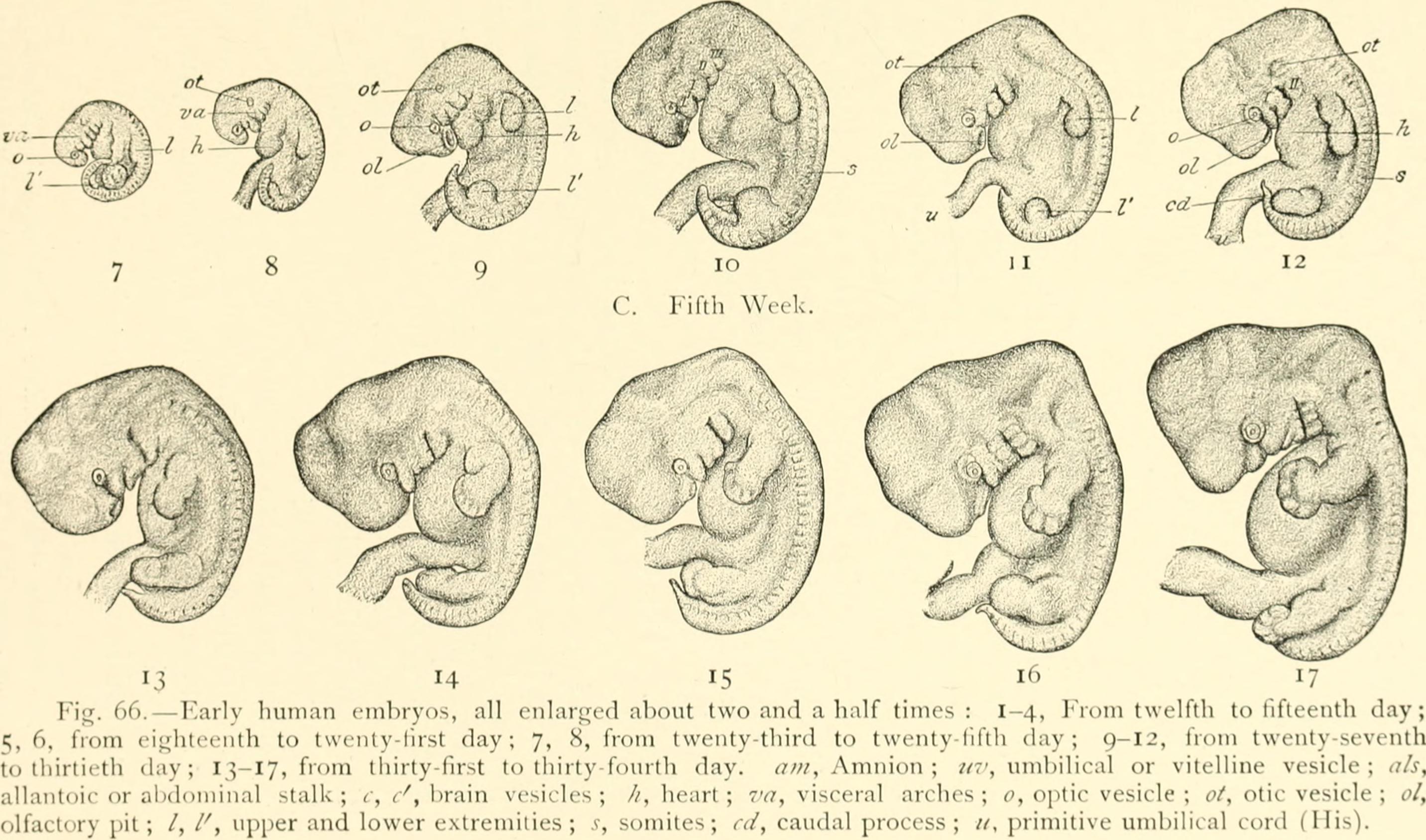
Embryology: The branch of biology and medicine concerned with the study of embryos and their development.
The lateral wall of each somite in a vertebrate embryo, giving rise to the connective tissue of the skin.

Somites (primitive segments) are precursor populations of cells that give rise to important structures associated with the vertebrate body plan and will eventually differentiate into dermis, skeletal muscle, cartilage, tendons, and vertebrae.
An embryo is an early stage of development of a multicellular diploid eukaryotic organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, an embryo develops from a zygote, the single cell resulting from the fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell.
Conception is the time when sperm travels up through the vagina, into the uterus, and fertilizes an egg found in the fallopian tube. Conception — and ultimately, pregnancy.
Zygote is the union of the sperm cell and the egg cell. Also known as a fertilized ovum, the zygote begins as a single cell but divides rapidly in the days following fertilization. After this two-week period of cell division, the zygote eventually becomes an embryo.
Mitosis (my-TOH-sis) is the dividing of all other cells in the body. It's how a baby in the womb grows. Mitosis causes the number of chromosomes to double to 92, and then split in half back to 46. This process repeats constantly in the cells as the baby grows.
Implantation is the stage of pregnancy at which the embryo adheres to the wall of the uterus. At this stage of prenatal development, the conceptus is called a blastocyst. It is by this adhesion that the embryo receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother to be able to grow.
A germ layer is a group of cells in an embryo that interact with each other as the embryo develops and contribute to the formation of all organs and tissues. All animals, except perhaps sponges, form two or three germ layers. The germ layers develop early in embryonic life.
Endoderm is one of the germ layers formed during animal embryonic development. Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastrula, which develops into the endoderm. Endoderm cells give rise to certain organs, among them the colon, the stomach, the intestines, the lungs, the liver, and the pancreas.
Mesoderm (middle), which lies between the endoderm and the ectoderm, give rise to all other tissues of the body, including the dermis of the skin, the heart, the muscle system, the urogenital system, the bones, skeleton, and the bone marrow (and therefore the blood).
Ectoderm(outside) The ectoderm, on the other hand, eventually forms certain “outer linings” of the body, including the epidermis (outermost skin layer) and hair and nervous system i.e neural cells.
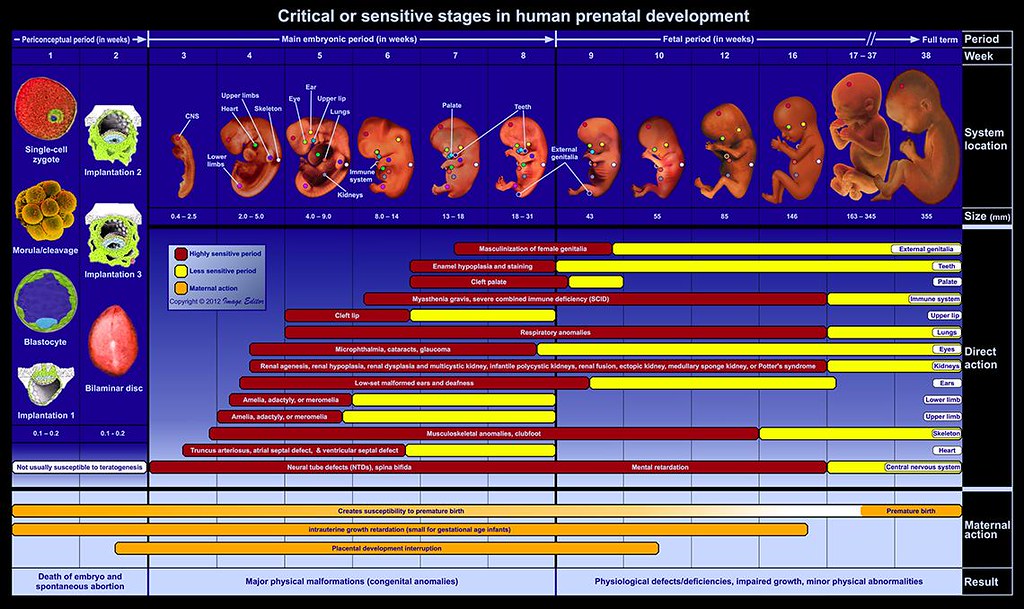
Teratogen: An agent or factor which causes malformation of an embryo.
Physiological Flexion: As babies develop and grow in the uterus they become folded up with their arms and legs flexed in towards their body. This position, along with the baby pushing against the walls of the uterus, creates what is called physiological flexion and provides the baby with flexed muscle tone in their limbs shortly after birth which slowly goes away outside of the womb. Gravity will influence the flexed position.
Pregnancy lasts for about 280 days or 40 weeks. A preterm or premature baby is delivered before 37 weeks of your pregnancy. Extremely preterm infants are born 23 through 28 weeks.
Neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. During the process, neural stem cells differentiate—that is, they become any one of a number of specialised cell types—at specific times and regions in the brain.
Motor development refers to the development of a child's bones, muscles and ability to move around and manipulate his or her environment. Motor development can be divided into two sections: gross motor development and fine motor development.
Motor learning is a loosely defined term that encompasses motor adaptation, skill acquisition, and decision-making (Shadmehr and Wise, 2005; Krakauer, 2006).
Motor control is the regulation of movement in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes reflexes as well as directed movement.
General movements (GMs): Are the most frequently occurring specific movement patterns of the fetus and young infant are the GMs are movements in which all parts of the body participate. During the past decade, it became increasingly clear that the quality of GMs reflects the integrity of the young nervous system.
The mid and term fetus develops in an environment where the effect of gravity is diminished by the presence of amniotic fluid.
Antigravity movements: any movements against gravity, planes of movement of the head, shoulder girdle, trunk, pelvis, limbs in the presence of gravity.
Chronological age refers to the actual amount of time a person has been alive. In other words, the number of days, months or years a person has been alive does not change, regardless of how healthy a lifestyle — even one filled with great exercise and nutrition habits — they are living.
Gestational age is the number of weeks that a baby has been in the uterus. A full-term pregnancy is usually 40 weeks. It's important to assess if gestational age is uncertain or if your baby is smaller or larger than expected. The new Ballard score is commonly used to determine gestational age.
Corrected age is a term most appropriately used to describe children up to 2 years of age who were born preterm (Fig 1). This term is preferred to “corrected gestational age” or “gestational age” and represents the age of the child from the expected date of delivery.
Developmental milestones are behaviours or physical skills seen in infants and children as they grow and develop. Rolling over, crawling, walking, and talking are all considered milestones. The milestones are different for each age range. There is a normal range in which a child may reach each milestone.
Birth History: Gestational age at birth weeks. Weight at birth (kg). Multiple birth Yes No Details: Pregnancy, delivery and Any maternal insults [alcohol, smoking] or illnesses during gestation. Where born: city, hospital. Mode of delivery, difficulties in delivery. Resuscitation, intensive care requirement at birth. Cyanosis, pallor, jaundice, convulsions, birthmarks, malformations, feeding or respiratory difficulties. Apgar score at birth if known. How baby was fed in first few days. Whether child went home with mother. Nutritional history.
Pregnancy lasts for about 280 days or 40 weeks. A preterm or premature baby is delivered before 37 weeks of your pregnancy. Extremely preterm infants are born 23 through 28 weeks.
1000 days of human development The first 1000 days of life the spanning from conception until second birthday, a unique period of opportunity when the foundations of optimum health, growth and neuro developmental across the lifespan are established, includes pregnancy.
Most babies get into a vertex, or head down, position near the end of your pregnancy, between 33 and 36 weeks normal vertex delivery: In a vertex delivery, the top of the baby's head comes first. The vertex here refers to the top of the head. A normal delivery is, in other words, a completely natural delivery of a baby by the mother without any medical intervention. During normal/vaginal delivery the primary focus is on how and in which position will the mother be comfortable delivering the baby.
Breech: About 3-4 percent of all pregnancies will result in the baby being breech. A breech pregnancy occurs when the baby (or babies!) is positioned head-up in the woman's uterus, so the feet are pointed toward the birth canal.
Natural method of birth is when the foetus comes through the birth canal out the vagina, The average length of a hospital stay for a normal vaginal delivery is 36–48 hours or with an episiotomy (a surgical cut to widen the vaginal canal) 48–60 hours, whereas a C-section is 72–108 hours.
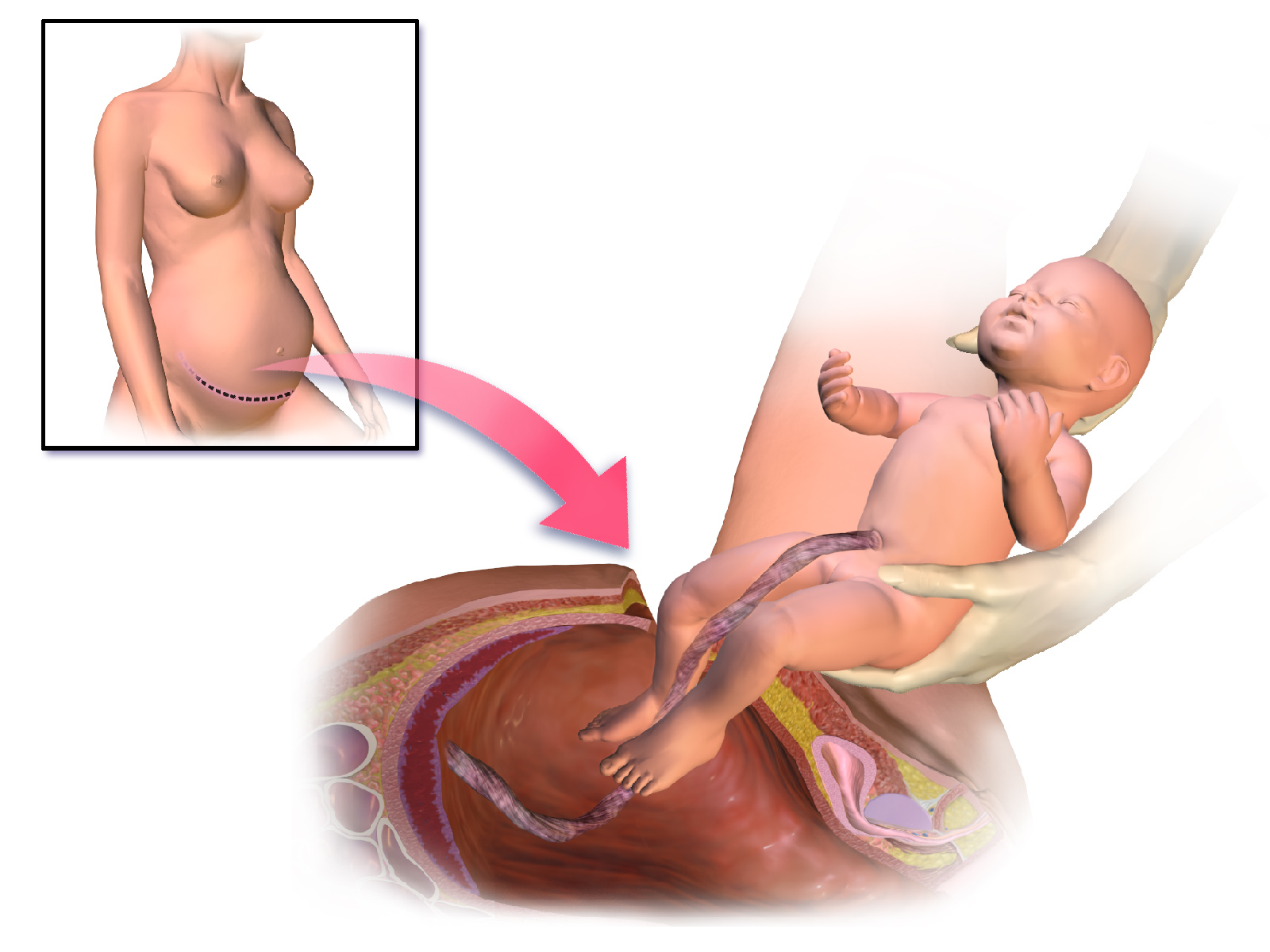
Cesarean delivery (C-section) is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. A C-section might be planned ahead of time if you develop pregnancy complications or you've had a previous C-section.
Prematurity is a term for the broad category of neonates born at less than 37 weeks' gestation. ... For premature infants born with a weight below 1000 g, the three primary causes of mortality are respiratory failure, infection, and congenital malformation.
Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, neuroplasticity, or neural plasticity, is the ability of the brain to change continuously throughout an individual's life, e.g., brain activity associated with a given function can be transferred to a different location, new neural pathways may and do form with repeated stimulation.
APGAR score: Is a method to quickly summarize the health of new-born children against infant mortality. s a test given to new-borns soon after birth. This test checks a baby's heart rate, muscle tone, and other signs to see if extra medical care or emergency care is needed. The test is usually given twice: once at 1 minute after birth, and again at 5 minutes after birth.
Foetus: is the unborn offspring of an animal that develops from an embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilisation and continues until birth.
Tummy time - It is essential for babies to be placed in prone position, as children who lack sufficient time in prone present with motor delays Especially head control, rolling, sitting, creeping, crawling and pulling up to standing are delayed in children who don’t spend enough time on their tummy. - Importance of tummy time on development of hand-eye coordination, fine motor skills and balance in later life . - Sensory input: prone position also stimulates vision and interaction with the environment. - Prevention of torticollis and/or plagiocephaly (flattened skull).
Cruising: Within a few weeks of learning to pull himself to a standing position, the baby will probably start shuffling along while holding onto furniture; this can start anywhere from 8 to 11 months. Called cruising, it's one of the last steps on the journey toward walking independently.
Pull to sit: The child assists the mom to pull himself into a sitting position using both or one of his arms.
Pull to stand: The child assists the mom to pull himself into a standing position using furniture/ both or one of his arms and legs to assist him to stand.

Prone lying: Is when the child is lying on their tummy with chest in contact with the surface.
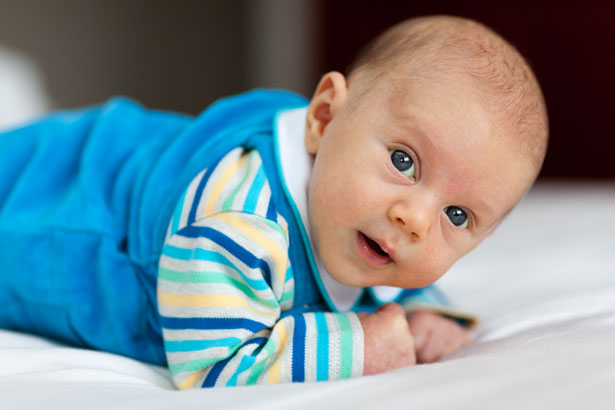

Puppy prone: Position in prone while weight bearing on the elbows, great starting position to strengthen neck, trunk extensors.
Facilitation: use of the therapists hands ,voice or environment to make active movements easier or to make them possible.
Starting positions: means the position of the body relative to the supporting surface at the beginning of an intervention and where the desired ending position of the body will be once task is completed will determine the difficulty/ease of the activity. 5 fundamental starting positions: lying prone or supine, side lying, sitting (ring, half, w-sit, long sit) four point or two point kneeling, standing.
Key Points of Control: parts of the human body (head, pelvis, trunk, shoulder girdle) from where the therapist can most effectively control and change patterns of movement in other parts of the body. They can be used for modification, facilitation, or stimulation. E.g placing therapists hand on the flexed knee(dissociation at pelvis) to facilitate rolling.
Reciprocity: the practice of exchanging things with others for mutual benefit, especially privileges granted by one country or organization to another. By imitating and talking with the baby, the parent allows their mutual exchanges to become a synchronized play of signals. This helps the baby to develop reciprocal skills. By continually being exposed to his parent's varied visual and verbal input, the baby learns to direct his or her attention to the outside world.
Gross motor skills involve movements of the large muscles of the arms, legs and torso. Kids rely on gross motor skills for everyday activities at school, at home and in the community. Kids who struggle with gross motor skills have trouble doing whole-body movements like climbing.
Outcome measure:is a tool used to assess a patient's current status. Outcome measures may provide a score, an interpretation of results and at times a risk categorization of the patient. Prior to providing any intervention, an outcome measure provides baseline data.
Population group: known as a well-defined collection of individuals or objects known to have similar characteristics.
Immunization: or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an agent.
Weight-bearing is defined as the ability of the body to hold or bear its own weight in any given position. The gross motor development of the healthy child progresses from the horizontal position-supine/prone to the upright standing position. This weightbearing occurs initially involving large surface area of the infant's body, in large surfaces/bases of support progressing to smaller or several points of contact with the infant's body to smaller base of support/surface area.
Posture observe head, shoulder, trunk, pelvis and limbs in each position. Posture begins in the newborn is in flexion of the extremities closely adducted to the trunk(physiological flexion in supine. Posture progresses from positions that require less support from body surface area, greater muscle strength, muscle co-ordination and balance.
Normal Tone: Defined as slight constant tension of healthy muscles (Kandel, Schwartz& Jessel 1991).
Range of motion: is the measurement of movement around a joint.
Passive range: of motion requires full assistance for an individual to move their joint.
Active-assistive requires partial assistance, and active range of motion is when the client is able to move their joint independently.
Hypertonia: Muscle overactivity that occurs when communication between the brain and nerves is affected by injury or illness. The neural component is called spasticity and is the inability to turn off the electromyographic at rest (no inhibitory stimuli)Which results in hyper-reflexia, cant modulate force. Results in altered muscle length(shortening) due non-neural components and joint alignment.
Weight-bearing is defined as the ability of the body to hold or bear its own weight in any given position. The gross motor development of the healthy child progresses from the horizontal position-supine/prone to the upright standing position. This weightbearing occurs initially involving large surface area of the infants body, in large surfaces/bases of support progressing to smaller or several points of contact with the infants body to smaller base of support/surface area.
Posture observe head, shoulder, trunk, pelvis and limbs in each position. Posture begins in the new-born is in flexion of the extremities closely adducted to the trunk(physiological flexion) in supine. Posture progresses from positions that require less support from body surface area, greater muscle strength, muscle co-ordination and balance.
Antigravity movements: any movements against gravity, planes of movement of the head, shoulder girdle, trunk, pelvis, limbs. Poor selective motor control. Abnormal motor sequences and synergies. Absent or poorly developed postural reactions: The abnormal interaction between three systems - somatosensory, visual and vestibular - is believed to be the cause of abnormal postural reactions.
Centre of gravity is imaginary balancing point where the body weight can be assumed to be concentrated and equally distributed. Can also be called Centre of mass.
Balance: an even distribution of weight enabling someone or something to remain upright and steady, In biomechanics, balance is an ability to maintain the line of gravity of a body within the base of support with minimal postural sway. Sway is the horizontal movement of the centre of gravity even when a person is standing still.
Static balance is the ability to maintain postural stability and orientation with centre of mass over the base of support and body at rest.
Dynamic balance is the ability to maintain postural stability and orientation with centre of mass over the base of support while the body parts are in motion.
Balance: Static (when person is stationery) or Dynamic(when person is in motion) Equilibrium reactions provide balance when the centre of gravity is disturbed.
Protective reactions are required to prevent injury if the equilibrium reactions are unable to restore balance. Protective reactions emerge first to the front, then the side and then backwards.
Equilibrium reactions are patterns which maintain balance of the whole body in the dynamic relationship between the shifting of one's centre of gravity through space and one's base of support.
Developmental delay: means a delay in one or more of the following areas: physical (gross motor, fine motor) development; cognitive development; communication; social or emotional development; or adaptive [behavioural] development.
The condition of a child being less developed than is normal for child's age (range of acquiring developmental milestones)
It is usually temporary if reason for delay is reversable but may be permanent if reason for delay persists even with treatment (developmental disability).
Adolescence is used to describe the transition from childhood to adulthood.
Puberty on the other hand refers to the time period during which physical changes occur.
Period during which adolescents reach sexual maturity and become capable of sexual reproduction.