 |
| Module 3: Toxicology - Section 9: Organic Solvents |
| TOX 9.2: Lecture: Health Effects of Organic Solvents |
 |
| Module 3: Toxicology - Section 9: Organic Solvents |
| TOX 9.2: Lecture: Health Effects of Organic Solvents |
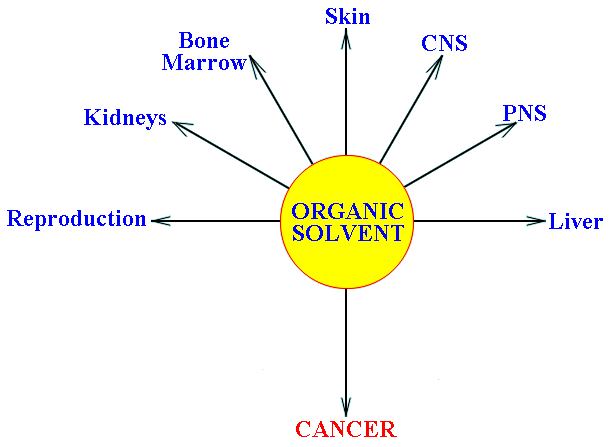
Effects common to most solvents.
This is often overlooked. Workers may complain of their eyes and noses running, sore throat, burning chest and cough.
With short-term relatively high exposures, headaches, mild euphoria, dizziness, nausea, fatigue.
Defat skin, may cause irritant contact dermatitis.
Effects specific to one or more individual solvents.
| Euphoria, disinhibition Light-headed “dizzy” Headaches, nausea, fatigue |
|
| Impaired judgement | |
| Depressed consciousness, seizures | |
| Impaired performance | |
| [Note: solvent sniffing
(glues, petrol) |
|
| Impaired postural stability |
Prognosis: Reversible.
Prognosis: Reversible in early stages.
|
hexanedione | |
| sensorimotor (ascending) neuropathy |
Prognosis: partially/wholly reversible.
|
* High exposure * Short latency *Rx ® Recovery |
E.g. tubular enzymes in urine.
Acute/subacute/high exposure:
|
acute necrosis + steatosis | |
Chronic exposure
|
raised enzymes: AST ALT |
Benzene (not Benzine!)
![]() Aplastic anaemia
Aplastic anaemia![]() Leukaemia ?/ lymphomas (10 yr ave. latency)
Leukaemia ?/ lymphomas (10 yr ave. latency)
Bischloromethyl ether (BCME)
Chloromethyl / methyl ether (CMME)
Epichlorhydrin
![]() ? site
? site
Halogenated solvents
Teratogenesis
Most solvents cross placenta
![]() ? Effects on foetus
? Effects on foetus
Spontaneous abortion
? Risk (ethylene oxide)
Semen quality
Glycol ethers ![]() decreased sperm counts
decreased sperm counts

Postgraduate Diploma in Occupational Health (DOH) - Modules 3: Occupational Medicine & Toxicology (Basic) by Profs Mohamed Jeebhay and Rodney Ehrlich, Health Sciences UCT is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 2.5 South Africa License. Major contributors: Mohamed Jeebhay, Rodney Ehrlich, Jonny Myers, Leslie London, Sophie Kisting, Rajen Naidoo, Saloshni Naidoo. Source available from here. For any updates to the material, or more permissions beyond the scope of this license, please email healthoer@uct.ac.za or visit www.healthedu.uct.ac.za.
Last updated Jan 2007.
Disclaimer note: Some resources and descriptions may be out-dated. For suggested updates and feedback, please contact healthoer@uct.ac.za.