Content begins here
Main page content
Click to collapse
These activities will be covered in the WHO skill's session. This page provides an outline of expectations for both students and facilitators.
For Facilitators
The facilitators’ role in this course is essential. The facilitators need to provide context for students and need to provide them with the practical skills that every healthcare worker should have to provide high quality primary ear care.
The activities have been well described and provide a basic outline of what is expected from both facilitators and students.
Being a health professional is about more than diagnosing and treating conditions. Excellent health professionals should display the following attributes: professionalism, good communication skills, the ability to form collaborations with others, leadership, and health advocacy.
Much of health education focusses on knowledge. We would like to include professionalism, communication skills, collaborative ideas and health advocacy in this course.
We aim to improve professionalism by contextualizing the importance ear and hearing care and thereby discussing empathy and an approach to patients. And by facilitating their interaction with patients through the skills that they are required to learn, including history taking and counselling.
The students will be required to interview a patient with hearing loss. This is to determine the challenges and difficulties that the patients face and to engage with the patient and learn from the patient about various coping strategies. They will write an essay which will be peer reviewed.
Please read through the activity sheet. In addition to teaching students the following skills:
- Otoscopy
- Tuning fork tests
- Ear irrigation
- Dry mopping and ear wicking
- Ear drop installation
- The whisper test (adults and older children)
- Other hearing tests without equipment, depending on the age of the patient
Students need to participate in a group discussion (linked to Module 1) about how they felt watching the videos on hearing loss. Ask whether any family members or friends have hearing loss and discuss how this impacts the individuals’ life and that of their family.
|
Activity 1 – defer |
|
Activity 2 – Examining the ear Divide the participants into groups. Number of groups will depend on the number of equipment sets available. So, if you have 5 otoscopes, you can divide into 5 groups.
|
|
Activity 3 – examining the ear (outer ear, ear canal) |
|
Activity 5: Discuss
|
|
Activity 6: Choose a partner. One is the ‘Health Care worker’ and one is the ‘Patient’. The patient chooses one of the problems from the list below and uses their imagination to make it sound like a typical patient from their clinic. The health care worker asks more questions about the problem and then uses their knowledge to describe what they might see if they were to examine the patient.
Discuss this and then present your problem to the group. Complete the patient’s health card. Fill in the patient details. Write in details of the problem. Circle each finding of the examination. WHO COULD THE PATIENT BE REFERRED TO? |
|
Activity 7:
Before learning more about ear infections and their treatment, please revise Practical B on otoscopic examination and practical D on dry mopping |
|
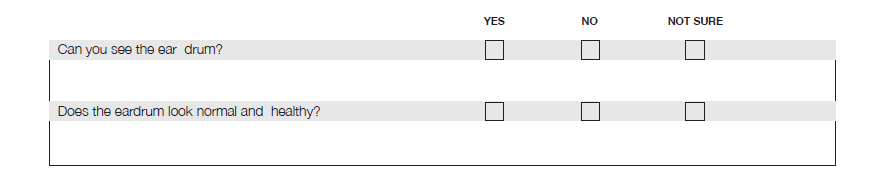
Activity 8: Examining the eardrum Use an otoscope to examine the ears of the other participants in your group.
Can you see the eardrum? Yes/no/unsure Does it look normal and healthy? Yes/no/unsure |
|
Activity 9: Examining the eardrum [when otoscopes are not available] Discuss the following with your trainer:
Try look in the ear canal with the help of a torch or strong light.
If you are certain that what you are looking at is the eardrum, and you are not certain what the problem is, refer the patient to a doctor or medical centre for assessment.
Examine carefully to understand what you are seeing and decide the possible diagnosis and management.
What would you do if you were not sure if the eardrum is normal and healthy? |
|
Activity 10: Discuss the following points about your dry mop/wick with your group and teacher
Ensure that the cotton is firmly attached to the stick and that it doesn’t slide out before inserting it into the ear. If it is not tightly attached, it could come off in the patients ear. What would happen if it did? It needs to be immediately removed, if not it could cause an infection.
You can remove it. Do so gently if you are able to get a grip on the cotton. In case it is too deep, then you need to send the person to a doctor for removal.
The tip can injure the skin of the ear canal, or (if pushed in deep) injure the eardrum (which may perforate the eardrum).
Inserting anything into the ear could cause infection, including cloth, unclean cotton, tissue paper etc.
To avoid any chance of passing germs from your hand to the patient, causing infection. |
|
Activity 11: Divide the participants into groups of two. One can be the health worker and the other is the parent of a child with discharging ear or have a discharging ear herself. The health worker to give proper instructions to the patient or parent using the community resource. |
|
Activity 12: Divide the participants into two groups. Ask each group to list out simple steps for preventing hearing loss in the community. Each group should make a list. [ [Then have a common discussion with both groups presenting their points of view.] ] |
|
Activity 13: Divide participants into groups of four or five and ask them to discuss how hearing loss and ear diseases can be prevented in the community. Then large group discussion (10min and 10 min) |
|
Activity 14: Discussion
|
|
Activity 15:
|
|
Activity 16:
|
|
Activity 17: Divide participants into groups of four or five and ask them to discuss what they could possibly do to improve ear and hearing care within their community. |
Divide the participants into two groups. Ask each group to list simple steps for preventing hearing loss in the community. Each group should make a list. Then have a common discussion with both groups presenting their points of view. Students should later, also engage in a discussion on the role of healthcare workers in ear and hearing care.
After this session they will be required to participate in an online forum discussion about easy, practical and innovative ways that primary level healthcare workers can improve patient education, improve healthcare and access to healthcare. The forum discussion will be where students attempt to provide ideas/solutions to this problem. Participation is compulsory and students will be given a mark out of 3 (depending on the quality of their suggestions). [note: this is Module 9 discussions].
Activity 2: Examining the ear
Participants should fill in the forms below
Did you examine both sides or only one? Describe findings on one side below
Activity 3
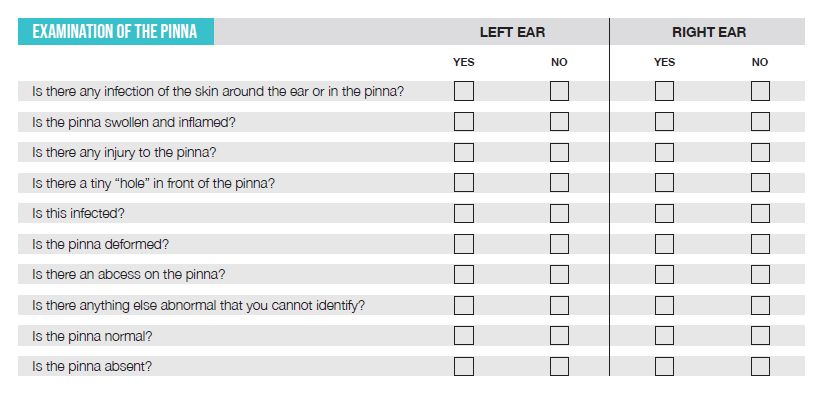
What can you see when you examine the pinna? Choose a partner and look at both ears of your partner and examine the pinna Mark off each your findings on the examination chart.
Choose a partner and look at both ears of your partner and examin the pinna. Mark off each of your findings on the examination chart.
[Discuss with your trainer what you have seen and any difficulties that you have had.]
Activity 4
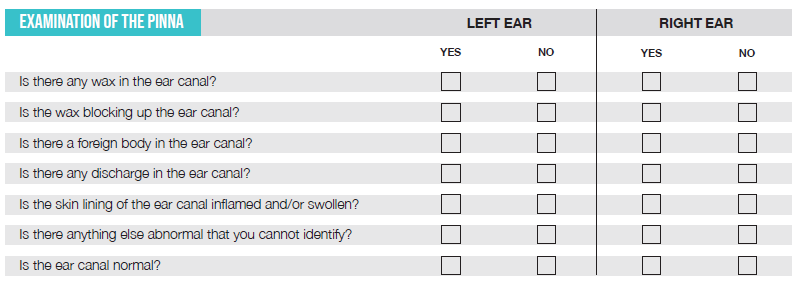
Choose a partner. Use an otoscope to examine both ear canals of your partner.
[Discuss what you have seen and any difficulties that you have had with your trainer.]
Activity 6
Choose a partner. One is the ‘Health Care worker’ and one is the ‘Patient’. The patient chooses one of the problems from the list below and uses their imagination to make it sound like a typical patient from their clinic. The health care worker asks more questions about the problem and then uses their knowledge to describe what they might see if they were to examine the patient.
Some suggested patient problems:
- Mother thinks child has put something into the ear.
- Patient has been swimming in dirty water. Ear now discharging.
- Mother brings a child who has severe pain in the ear, especially while touching.
Discuss this and then present your problem to the group.
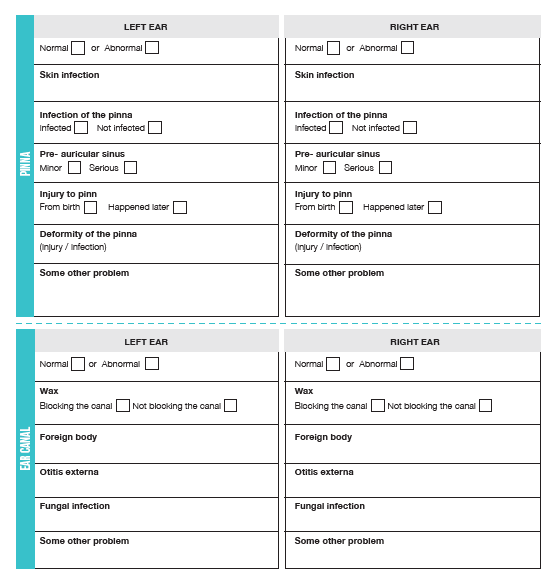
Complete the patient’s health card. Fill in the patient details. Write in details of the problem. Circle each finding of the examination.
WHO COULD THE PATIENT BE REFERRED TO?
Patients who cannot be treated or patients who have a problem but you do not know what it is should be referred to someone with more experience – a more highly trained nurse, a clinical assistant, a nurse or clinical practitioner or a doctor. If someone with more experience is not available or if the case is urgent then refer the patient to your local hospital.
ALWAYS CHECK BOTH EARS!
Activity 8: Examining the eardrum
Use an otoscope to examine the ears of the other participants in your group.
Hold the otoscope like a pencil in your hand. Some otoscopes are difficult to hold like this; if that is the case, hold the otoscope in a fist.
Then, do the following to properly examine the eardrum:
- Pull the pinna back and up to straighten the ear canal.
- Move the tip of the speculum around gently until you can see the whole of the eardrum.
- Answer these questions while you are looking at the eardrum.
Important tips: Use a speculum that is large enough to see through and is comfortable for the size of the ear canal.
If you cannot see the eardrum or are not sure, then discuss it with your trainer.