|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Tania
Douglas, Ernesta Meintjes
Collaborators:
Denis
Viljoen – Foundation for Alcohol-Related
Research
Postdoctoral
fellow: Mahesh Veezhinathan
Completed student projects: o
Rex Grobbelaar (MSc,
2005) Stereo facial image matching to aid in fetal alcohol syndrome screening o
Tinashe Mutsvangwa
(MSc, 2006) Statistical analysis of facial
landmark data for optimization of fetal alcohol
syndrome diagnosis Current student projects: o
Tinashe Mutsvangwa,
Stereophotogrammetric facial analysis for diagnosis of fetal
alcohol syndrome in infants o
Mahalingam Veeraragoo, Pattern recognition to detect fetal alcohol syndrome in stereo facial images Description: Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), which occurs as
a consequence of excessive maternal alcohol ingestion during pregnancy, is
one of the most common preventable causes of mental retardation worldwide. The highest prevalence of
FAS worldwide has been found among first-grade children in a wine-growing
region in the
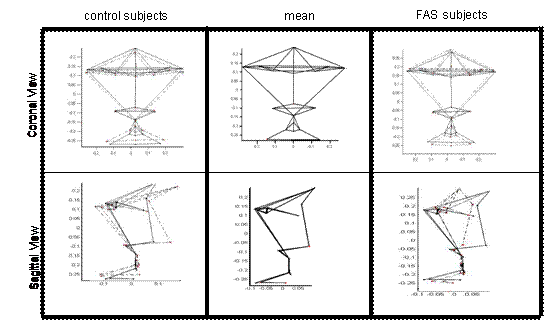
Landmark-based facial
shape variation between children with fetal
alcohol syndrome and control subjects; application of generalised Procrustes analysis and principal component analysis. The solid line indicates the
mean facial shape across all subjects. The dotted lines indicate the
normal shape and the FAS shape in the left and right columns,
respectively. Features of interest: o
Underdeveloped midface o
Microcephaly o
Longer and slightly smoother philtrum o
Shorter outer canthal distances o
Small palpebral fissure lengths Recent publications: Journal papers: – E.M. Meintjes, T.S.
Douglas, F. Martinez, C.L. Vaughan, L.P. Adams, A. Stekhoven,
D. Viljoen. A stereo-photogrammetric
method to measure the facial dysmorphology of
children in the diagnosis of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Medical Engineering
& Physics, 24(10):683-689, 2002. – T.S. Douglas, F. Martinez, E.M. Meintjes, C.L. Vaughan, D. Viljoen.
Eye feature extraction for diagnosing the facial phenotype associated with
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing,
41(1):101-106, 2003. – T.S. Douglas, E.M. Meintjes,
C.L. Vaughan, D. Viljoen. The role of depth in eye
distance measurements: comparison of single and stereo-photogrammetry,
American Journal of Human Biology, 14(4):573-578, 2003. – T.S. Douglas. Image processing for craniofacial
landmark identification and measurement: a review of photogrammetry
and cephalometry. Computerized Medical Imaging and
Graphics, 28(7):401-409, 2004. – T.S. Douglas, D.L. Viljoen.
Eye measurements in 7 year-old black South African children. Annals of Human
Biology, 33(2):241:254, 2006. – R. Grobbelaar, T.S.
Douglas. Stereo image matching for facial feature measurement to aid in Fetal
Alcohol Syndrome screening. Medical Engineering & Physics, 29(4):459-464,
2007. – T.E.M. Mustvangwa, T.S.
Douglas. Morphometric analysis of facial landmark
data to characterize the facial phenotype associated with Fetal Alcohol
Syndrome. Journal of Anatomy, 210:209-220, 2007. Book chapter: – E.M. Meintjes, T.S. Douglas.
Diagnosis of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
measurement of the facial dysmorphology. In
Comprehensive Handbook of Alcohol Related Pathology, Eds:
V.R. Preedy and R.R. Watson, Academic Press, ISBN
0125643705, 2004. |
||||||||||||||