 |
| Module 3: Toxicology -
Section 4: Biological Monitoring |
| TOX 4.4: Lecture: Biological Monitoring and Biological Effect Monitoring - (Continued) |
EXAMPLE OF BIOLOGICAL MONITORING - INORGANIC LEAD:
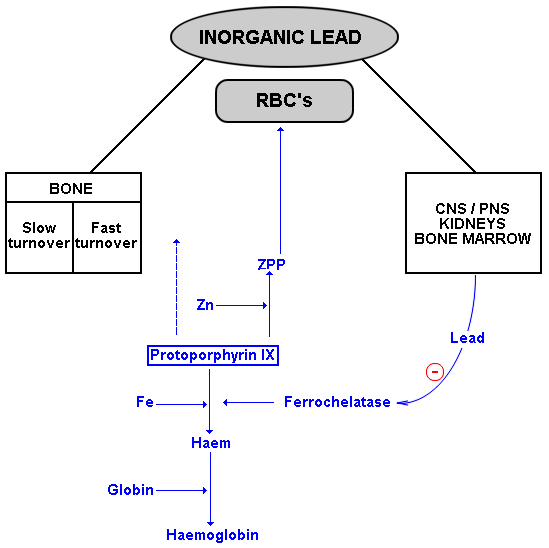
- Legislated schedule including medical removal. (See OHSA- Regulations: Lead Regulations, 2001.)
- Four compartment kinetics: blood, soft tissues, trabecular bone, cortical bone.
- Interpretation of a given blood lead is different in new as vs long service workers.
- Interlaboratory differences may be substantial (See the graph).
EXAMPLE OF BIOLOGICAL EFFECT MONITORING:
- Use individual baseline as reference!
- Normal variation, i.e. in absence of exposure: 10-15%.
- 2-3 month recovery, i.e. return to baseline in absence of exposure.
BIOLOGICAL EFFECT MONITORING OF EXPOSURE TO POSSIBLE CARCINOGENS:
These tests are not used routinely but rather in toxicologic or epidemiologic research.
- Urinary mutagens (Ames test)
- non-specific test of genotoxicity;
- smoking a confounder
.
- Haemoglobin and DNA-adducts e.g. benzo(a)pyrene
(Adduct = chemical bond)
- Specific but expensive. Doesn’t necessarily mean disease.
- Chromosomal abnormalities ("clastogenic"),
e.g. for ethylene oxide
- chromosomal aberrations;
- sister chromatid exchanges.
- Oncogene activation.



Postgraduate Diploma in Occupational Health (DOH) - Modules 3 – 5: Occupational Medicine & Toxicology by Prof Rodney Ehrlich & Prof Mohamed Jeebhay is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at http://www.healthedu.uct.ac.za/



