 |
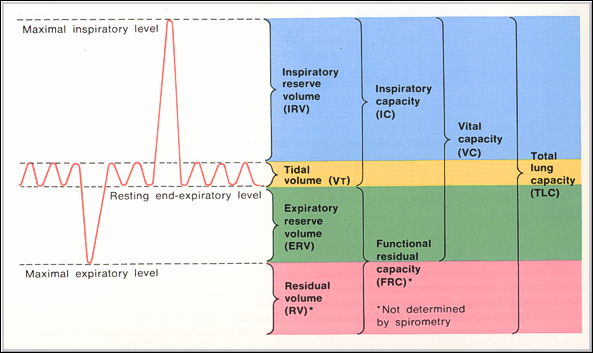
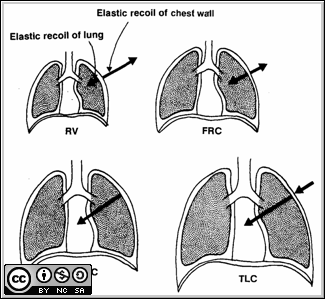
| Module 4: Physiology of the Respiratory System - Lung Volumes. |
 |
| Module 4: Physiology of the Respiratory System - Lung Volumes. |
Note the following:
|
 |

Postgraduate Diploma in Occupational Health (DOH) - Modules 3 – 5: Occupational Medicine & Toxicology by Prof Rodney Ehrlich & Prof Mohamed Jeebhay is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at http://www.healthedu.uct.ac.za/