This Schedule contains flow diagrams that provide guidelines to the procedures for the resolution of some of the more important disputes that may arise under this Act. This Schedule not part of this Act. It does not have the force of law. The flow diagrams are intended only to provide assistance to those parties who may become involved in a dispute.
The flow diagrams do not indicate the rights that parties may have to seek urgent interim relief, nor do they indicate the right of review or appeal that parties have to the Labour Court or the Labour Appeal Court in certain cases. This Act sets out the circumstances in which these rights are available.
Awards and determinations by arbitrators are enforceable ultimately by the Labour Court.
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
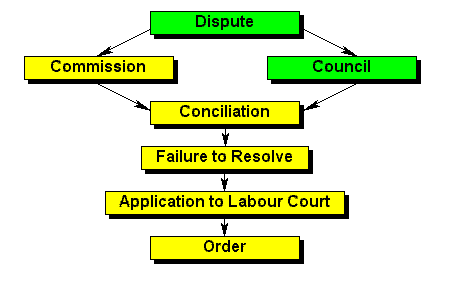
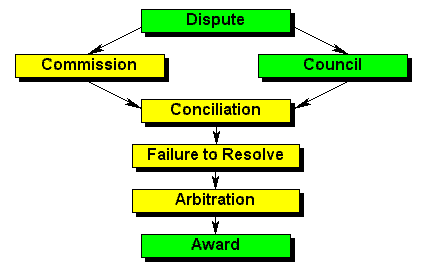
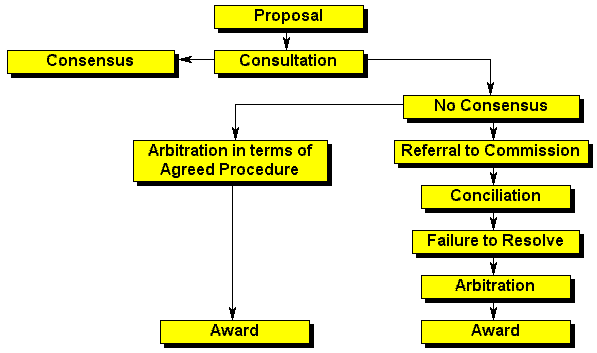
| Dispute | This procedure is relevant to the interpretation or application of Chapter II. For example, if an employer threatens to dismiss an employee unless the employee resigns from a trade union, that employee can enforce the rights conferred by this chapter in terms of the procedure. If a trade union threatens to boycott an employer, for example, because the employer institutes proceedings against the union, the employer can enforce the rights in the same way. |
| Council | The dispute must be referred to a council if the parties to the dispute fall within the council's registered scope. |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
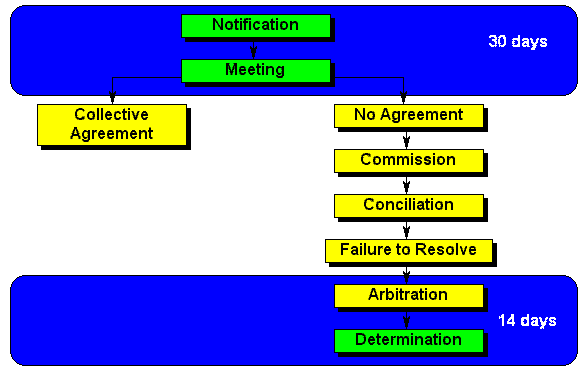
| Notification | A registered trade union may notify an employer that it intends to exercise organisational rights. The content of the notice is described in section 21(2). For example, if a registered trade union is sufficiently representative, it may notify the employer that it seeks to exercise the right of access. |
| Meeting | The object of the meeting is to conclude a collective agreement on the exercise of the organisational right. If there is no agreement, the trade union can elect to exercise a right to strike, or it can refer the dispute to the commission. If the trade union elects not to strike, it cannot refer a dispute over the organisational rights to the commission for a period of 12 months. |
| Determination | The Act contemplates disputes and therefore determinations about the definition of a workplace, the representativeness of the union and the manner in which organisational rights are exerted. |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
| Notification | |
| Meeting | |
| Determination |
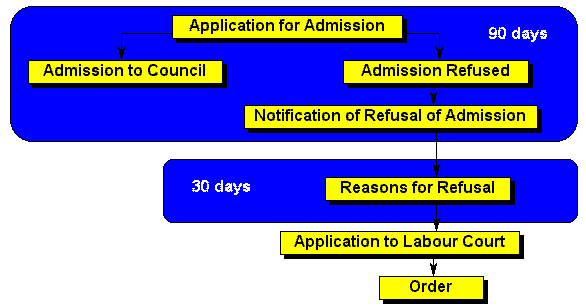
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
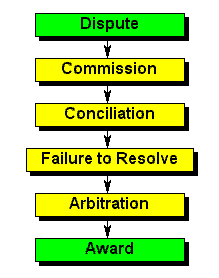
| Dispute | This procedure is about the interpretation or application of closed shop and agency shop agreements. For example, if the contributions deducted from wages in terms of those agreements are used for purposes other than those referred to in section 25(3)(d) or section 26 (3)(d), that dispute may be referred to the Commission. Dismissal disputes involving closed shops are dealt with in Chapter VIII - see diagram in Section 11 of this schedule |
| Award | Section 24(7) confers a limited right of appeal to the Labour Court against some awards. |
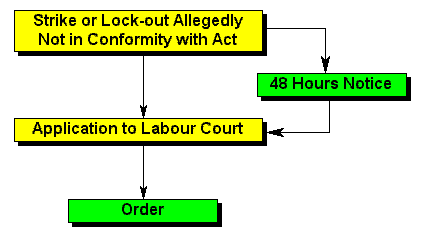
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
| 48 hr notice | The notice requirement is dealt with in section 68(2). Shorter notice may be permitted in the circumstances specified in that section. Notice is not required if the employees are engaged in an essential service or a maintenance service. |
| Order | The orders that the Labour Court may grant include restraining orders and an order for the payment of compensation. |
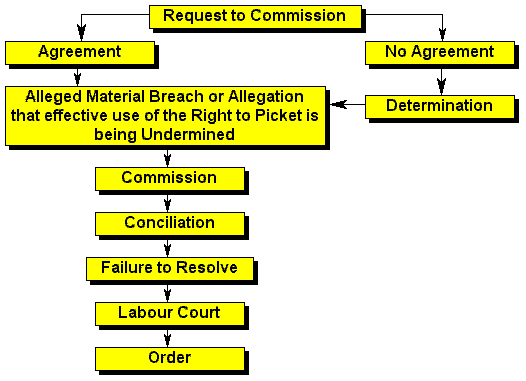
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
| Dispute | A dispute of interest in an essential service may, for example, include a dispute about wages. Because employees may not strike and employers may not lock out (see section 65(1)(d)) any party may refer the dispute to a council or the commission. |
| Council | The dispute must be referred to a council if the parties to the dispute fall within the council's registered scope. |
| Award | In the case of an award that binds the state and that has no financial implications, special Parliamentary procedures are prescribed. (See section 74(5 - 7)) |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
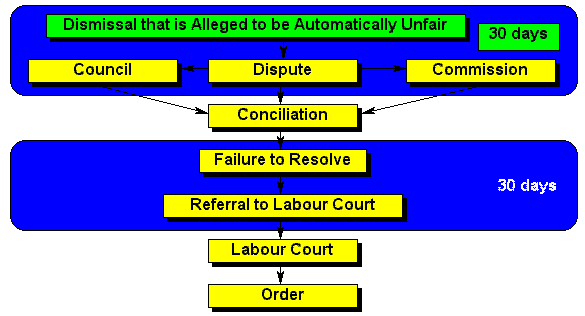
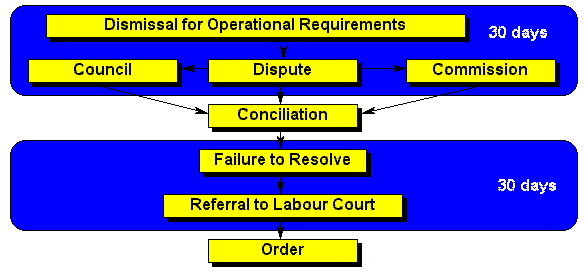
| Dismissal | Examples of dismissals that are automatically unfair include dismissal for participation in a protected strike, dismissal on account of pregnancy and dismissal that amounts to an act of discrimination. |
| 30days | The time limit is designed to ensure that disputes are dealt with as soon as possible. Condonation can be granted if there is good cause to do so. |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
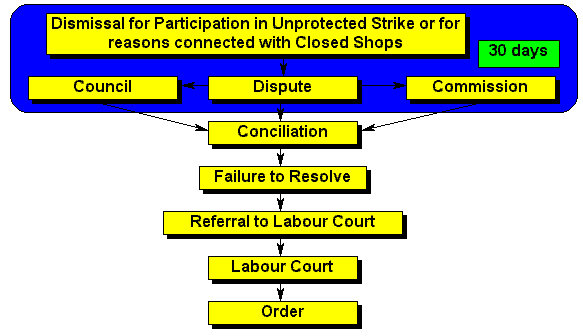
| Dismissal | The time limit is designed to ensure that disputes are dealt with as soon as possible. Condonation can be granted if there is good cause to do so. |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
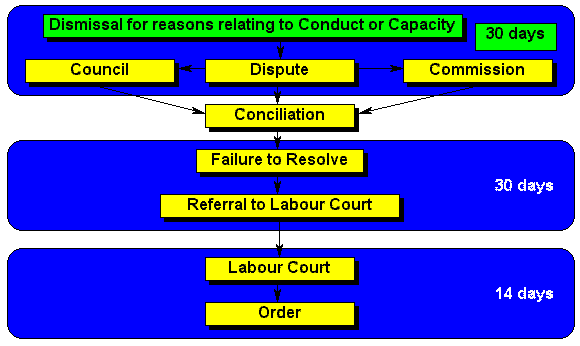
| Dismissal | Dismissal for misconduct and incapacity is dealt with in the Code of Good Practice: Dismisssal in Schedule 8. |
| 30days | The time limit is designed to ensure that disputes are dealt with as soon as possible. Condonation can be granted if there is good cause to do so. |
| Item | Note |
|---|---|
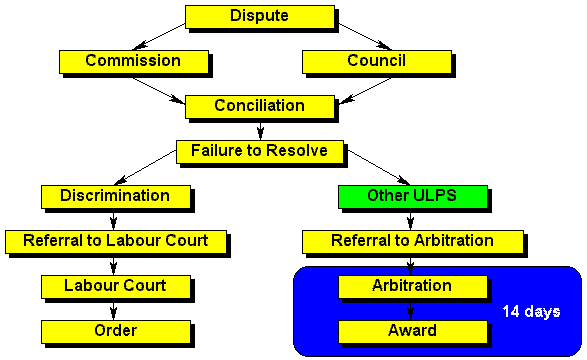
| Other ULPS | Other unfair labour practices include unfair conduct by the employer relating to promotion/demotion, training or the provision of benefits, unfair suspension, the failure to reinstate or re-employ an employee in terms of any agreement (see Item 2, Schedule 7). |
| The CHM file was converted to HTML by chm2web software. |